- 首发:2023-05-27 00:20:32
- 教程
- 4737
在本文中,我将向大家介绍如何在Windows平台上使用C++执行外部命令。我们将探讨两种不同的方法,并对它们进行比较和描述。当我们需要在程序中集成其他应用程序或运行脚本时,这两种方法都非常有用。
在详细讲解这两种方法之前,让我们先了解为什么我们需要在C++程序中执行外部命令。有时,我们需要与其他进程进行交互,例如运行一个脚本、启动一个新进程或收集系统信息。在这些情况下,执行外部命令可以帮助我们轻松地完成这些任务。
现在让我们开始深入了解这两种方法。
方法 1:使用_popen和_pclose函数
// 代码片段1(Method 1)
#include <array>
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
std::string exec(const char *cmd) {
std::array<char, 128> buffer;
std::string result;
FILE *pipe = _popen(cmd, "r");
if (!pipe) {
throw std::runtime_error("_popen() failed!");
}
while (fgets(buffer.data(), buffer.size(), pipe) != nullptr) {
result += buffer.data();
}
int exitStatus = _pclose(pipe);
if (exitStatus != 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("Command exited with non-zero status.");
}
return result;
}
int main() {
try {
// Replace "command" with your command
std::string aniCommand = "command";
std::string output = exec(aniCommand.c_str());
// Save output to file
std::ofstream outputFile("output.txt");
if (outputFile.is_open()) {
outputFile << output;
outputFile.close();
std::cout << "Output saved to file." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Error opening file." << std::endl;
}
} catch (const std::runtime_error &e) {
std::cerr << "Error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
该方法主要利用了Microsoft提供的_popen和_pclose扩展函数。该方法相对简单且易于理解。首先,我们使用_popen创建一个管道并与子进程关联;接着,我们读取子进程通过管道发送的输出。然后,我们关闭管道并检查子进程的退出状态。最后,我们将从子进程获取的输出保存到文件中。
优点
- 使用_popen和_pclose函数执行外部命令,较简单易懂。
- 将命令输出保存到文件中。
缺点
- 可能会遇到兼容性问题,因为_popen和_pclose是Microsoft扩展函数,可能不同编译器的支持程度有所差异。
方法 2:使用Windows API
// 代码片段2(Method 2)
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <windows.h>
std::string exec(const char *cmd) {
SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES sa;
sa.nLength = sizeof(sa);
sa.lpSecurityDescriptor = NULL;
sa.bInheritHandle = TRUE;
HANDLE hRead, hWrite;
if (!CreatePipe(&hRead, &hWrite, &sa, 0)) {
throw std::runtime_error("CreatePipe failed");
}
STARTUPINFO si;
ZeroMemory(&si, sizeof(si));
si.cb = sizeof(si);
si.dwFlags = STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW | STARTF_USESTDHANDLES;
si.hStdOutput = hWrite;
si.hStdError = hWrite;
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi;
ZeroMemory(&pi, sizeof(pi));
if (!CreateProcess(NULL, (LPSTR)cmd, NULL, NULL, TRUE, 0, NULL, NULL, &si,
&pi)) {
CloseHandle(hWrite);
CloseHandle(hRead);
throw std::runtime_error("CreateProcess failed");
}
CloseHandle(hWrite);
std::vector<char> buffer(4096);
DWORD bytesRead;
std::string output;
while (true) {
if (!ReadFile(hRead, buffer.data(), buffer.size(), &bytesRead, NULL)) {
break;
}
output.append(buffer.cbegin(), buffer.cbegin() + bytesRead);
}
CloseHandle(hRead);
CloseHandle(pi.hProcess);
CloseHandle(pi.hThread);
return output;
}
int main() {
// Ensure your command generates ANSI color codes
std::string output = exec("d:\\Project\\cpp-practice\\build\\cpp-practice."
"exe --gtest_color=yes 2>&1");
std::cout << output;
return 0;
}
与方法 1 相比,该方法提供了更多底层控制。这里,我们使用Windows API(CreatePipe、CreateProcess和ReadFile)来执行外部命令。首先,我们创建一个匿名管道;接着,我们创建一个新进程并将管道与其关联。然后,我们读取子进程通过管道发送的输出。最后,关闭管道以及相关进程和线程句柄。
优点
- 使用Windows API(CreatePipe、CreateProcess和ReadFile)来执行外部命令,更通用且适配多种编译器。
- 可以获取子进程stdout和stderr的输出。
缺点
- 代码相对复杂,需要处理更多底层Windows API细节。
- 没有将命令输出保存到文件中。
结论
在选择使用哪种方法时,应根据具体需求和目标进行权衡。如果你只需执行简单外部命令并保存输出结果到文件,那么方法 1 可能更适合你。然而,如果你需要控制更多底层细节或确保与不同编译器的兼容性,方法 2 可能是更好的选择。
两种方法均有其优点和局限性;最佳策略取决于你的具体需求和项目情况。希望本文能为你在Windows平台上使用C++执行外部命令提供帮助。在未来的编程实践中,你可以灵活地运用这些方法以达到预期目标。
暂无内容




老师你好,我希望能用一个openwrt路由器实现IPv4和IPv6的桥接,请问我该如何实现?我尝试了直接新增dhcpv6的接口,但是效果不甚理想(无法成功获取公网的ipv6,但是直连上级路由的其他设备是可以获取公网的ipv6地)
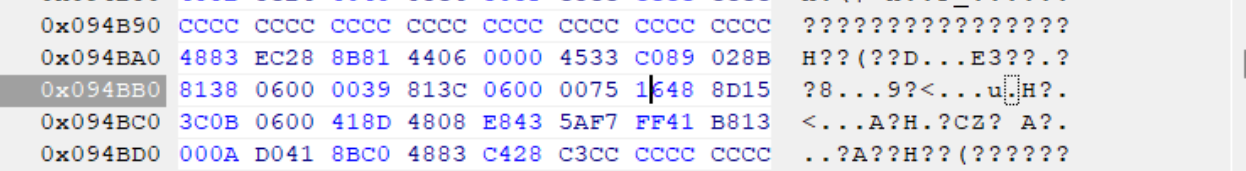你好
,为什么我这里是0039 813C 0600 0075 16xx xx xx,只有前6组是相同的,博客中要前8位相同,这个不同能不能照着修改呢?我系统版本是Win1124H2
大神你好,win11专业版24h2最新版26100.2033,文件如何修改?谢谢
win11专业版24h2最新版26100.2033,Windows Feature Experience Pack 1000.26100.23.0。C:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll系统自带的这个文件,39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 85 XX XX XX XX 替换为 B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90。仍然无法远程连接。原来是win11 21h2系统,是可以远程链接的。共享1个主机,2个显示器,2套键鼠,各自独立操作 各自不同的账号,不同的桌面环境。
博主,win11专业版24h2最新版,C:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll系统自带的这个文件,找不到应该修改哪个字段。我的微信:一三五73二五九五00,谢谢